In the dynamic world of finance, professionals are often faced with the decision of whether to start a new venture from scratch or to acquire an existing business.
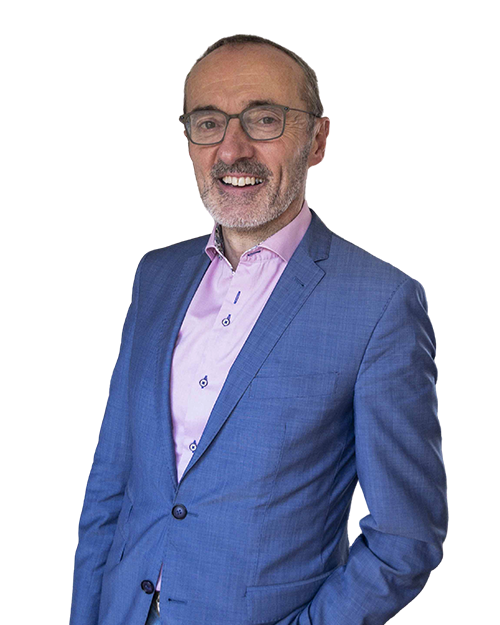
In Buying and Selling a Business, Cormac Lucey gave compelling reasons why buying a business can be a strategic move that offers numerous advantages.
Firstly, acquiring a business can present an opportunity for bargain buying. Companies may be available at a price below their intrinsic value due to various factors such as poor management or liquidity issues faced by the current owners. This allows buyers to obtain assets at a discount, potentially leading to significant cost savings and value creation.
Another key reason to consider an acquisition is the potential for synergies. When two companies merge, they may realise cost savings and efficiency gains that were not possible as separate entities. For example, firms operating in the same market can combine their operations to save on costs and improve their overall market position.
The concept of economies of scale also plays a crucial role in the decision to buy a business. Larger companies can often reduce their unit operating costs more effectively than their smaller counterparts. By merging with or acquiring another company, a firm can increase its size and market share, allowing it to compete more effectively and generate better returns.
In industries where technology evolves rapidly, acquiring a business can provide a technical advantage. Larger firms with more resources can acquire smaller companies that have made technological breakthroughs, thereby securing a competitive edge and protecting their market position.
Moreover, acquisitions can accelerate the winning of market position. Instead of building a new operation from the ground up, which can be time-consuming and costly, buying an existing business can offer a quicker and often more cost-effective way to gain market share.
Managerial motives should not be overlooked either. The management of the acquiring firm may pursue acquisitions for reasons such as increased remuneration, status, and power that come with successful deals.
Lastly, there are other benefits to consider, such as risk diversification, potential tax advantages, and the protection of market position. These factors contribute to the overarching goals of fostering company growth, strengthening competitive stances, and optimising returns for shareholders.
Buying a business can be a highly strategic move for finance professionals looking to expand their portfolio, enter new markets, or consolidate their position in an industry. The potential for bargain purchases, synergies, economies of scale, technical advantages, accelerated market positioning, managerial benefits, and other financial incentives make acquisitions a compelling option in the pursuit of business success.
For the full session, please click here. In this course, Cormac Lucey covers the following topics;
- Steps in a transaction
- Head of agreement
- Due diligence
- Legal documentation
- The MBO market & recent transactions
The contents of this article are meant as a guide only and are not a substitute for professional advice. The author/s accept no responsibility for any action taken, or refrained from, as a result of the material contained in this document. Specific advice should be obtained before acting or refraining from acting, in connection with the matters dealt with in this article.